
The double-entry practice ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the left-side value of the equation will always match the right-side value. The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet. This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends. Here we can see the list of all assets that have been reported on Hershey company balance sheet for 2023. Better decisions can be made by creditors, analysts, and investors by knowing the subtleties of the extended accounting equation and its repercussions. Evaluation by CreditorsLenders and creditors can use the expanded equation to evaluate how a company allocates its funds and manages its financial resources over time.
Accounts Payable
In accounting, we have different classifications of assets and liabilities because we need to determine how we report them on the balance sheet. The first classification we should introduce is current vs. non-current assets or liabilities. The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business. In accounting, the claims of creditors are referred to as liabilities and the claims of owner are referred to as owner’s equity. In our examples below, we show how a given transaction affects the accounting equation.
What Is the Expanded Accounting Equation?
HighRadius Solution empowers organizations to experience enhanced efficiency by leveraging the best of the latest accounting technology. Also, the extended accounting equation is essential for promoting accountability, openness, and efficient decision-making. Let’s look at an example of the expanded version of the accounting accounting equation calculator equation. Impact of Net Income on EquityThe effect of net income on equity is readily apparent to analysts. This knowledge is essential for assessing the profitability and financial stability of the business. In this table, we will explore each element of the accounting equation and its relationship to the other two.
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
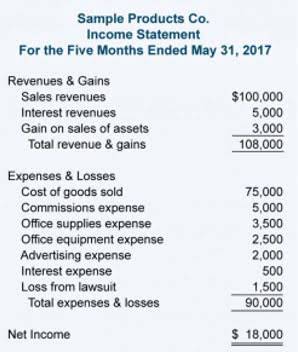
The accounting equation is often expressed as an accounting formula and states that the sum of liabilities and equity is always equivalent to the total assets of the organization. It is the fundamental foundation of accounting that ensures financial statement accuracy. The expanded accounting equation is a form of the basic accounting equation that includes the distinct components of owner’s equity, such as dividends, shareholder capital, revenue, and expenses. The expanded equation is used to compare a company’s assets with greater granularity than provided by the basic equation. Examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill.
From the accounting equation, we see that the amount of assets must equal the combined amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity. So whatever the worth of assets and liabilities of a business are, the owners’ equity will always be the remaining amount (total assets MINUS total liabilities) that keeps the accounting equation in balance. The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity.
The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position. As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets. So, as long as you account for everything correctly, the accounting equation will always balance no matter how many transactions are involved. The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system.

We show formulas for how to calculate it as a basic accounting equation and an expanded accounting equation. Created more than 500 years ago, the basic accounting equation continues to serve as the foundation of double-entry accounting. The double-entry system ensures that for every transaction recorded to an account as a debit, a corresponding entry must be entered to another account as a credit. The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity).
What is the Expanded Accounting Equation?
Double-entry accounting is a fundamental concept that backs most modern-day accounting and bookkeeping tasks. The expanded accounting equation can be rearranged in many ways to suit its use better. With that being said, no matter how the formula is laid out, it must always be balanced. In this expanded accounting equation, CC, the Contributed Capital or paid-in capital, represents Share Capital. Retained Earnings is Beginning Retained Earnings + Revenue – Expenses – Dividends – Stock Repurchases. Accounting software is a double-entry accounting system automatically generating the trial balance.
Assets in Accounting: A Beginners’ Guide
- The accounting method under which revenues are recognized on the income statement when they are earned (rather than when the cash is received).
- Think of retained earnings as savings, since it represents the total profits that have been saved and put aside (or “retained”) for future use.
- For instance, if a business takes a loan from a bank, the borrowed money will be reflected in its balance sheet as both an increase in the company’s assets and an increase in its loan liability.
- This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1.
As the fintech industry continues to expand, memorizing accounting equations will become obsolete. The bread and butter lies in freeing up your human labor to work on value-based tasks, while automating manual processes. Incorrect classification of an expense does not affect the accounting equation.
- Liabilities are anything that the company owes to external parties, such as lenders and suppliers.
- Making the jump to double-entry accounting can be a scary prospect for business owners with no accounting experience, but the end result is worth the extra time it may take to get the concept down properly.
- Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
- The first classification we should introduce is current vs. non-current assets or liabilities.



یک دیدگاه بنویسید